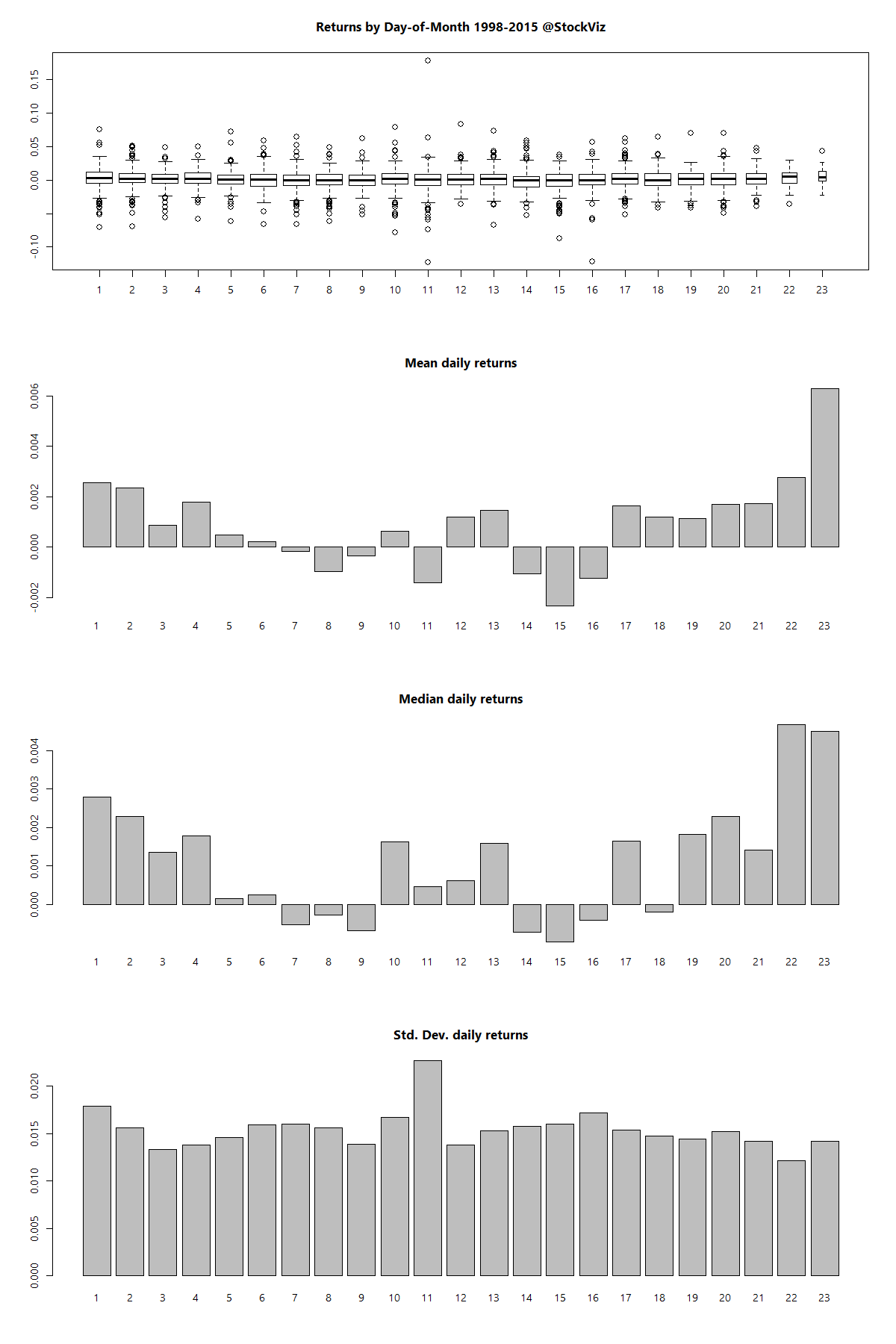
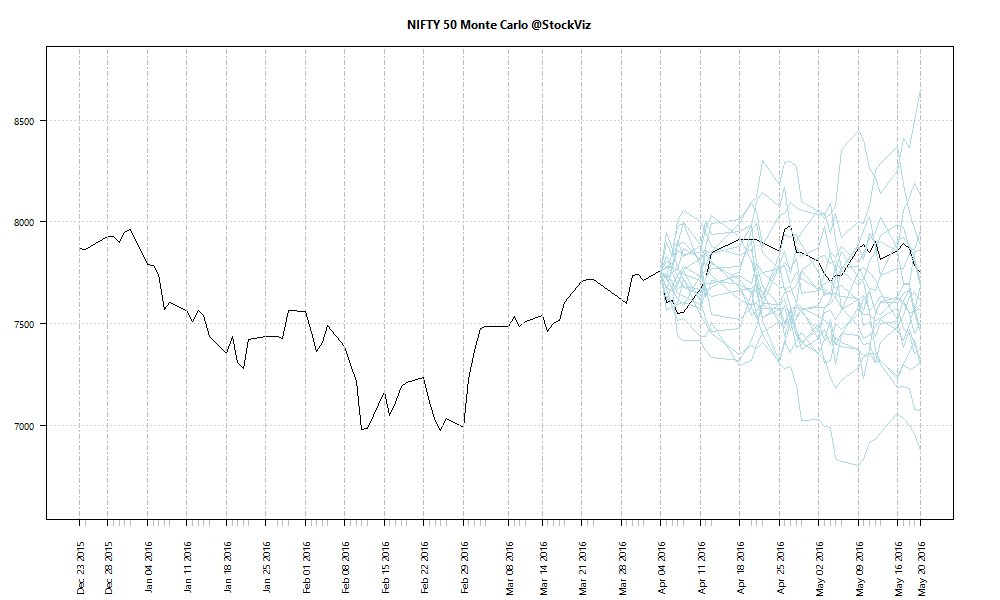
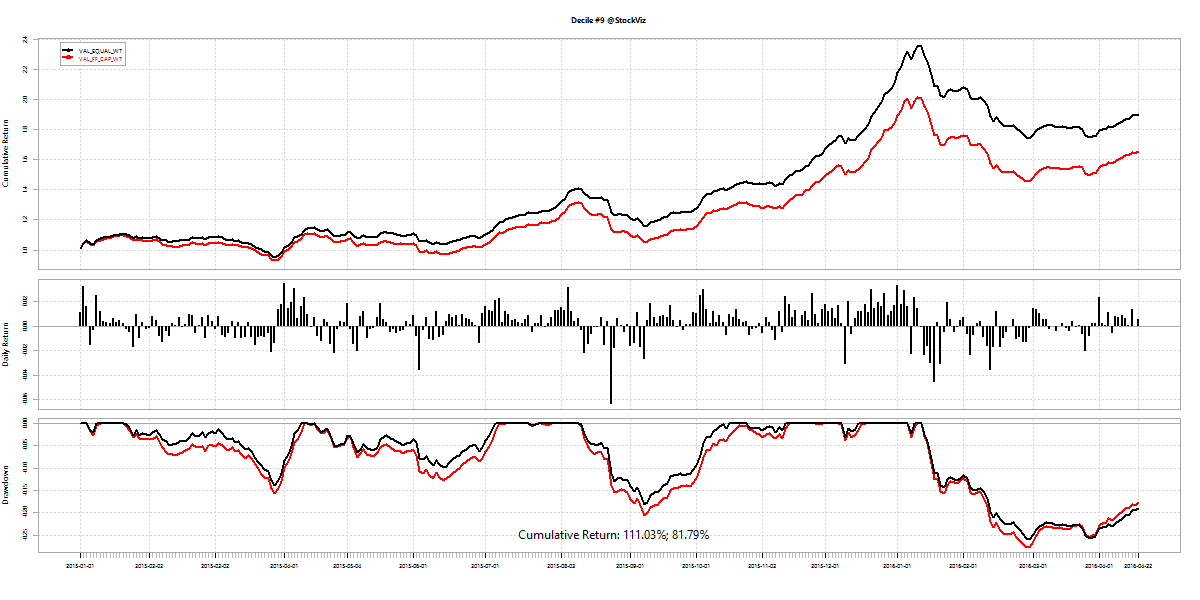
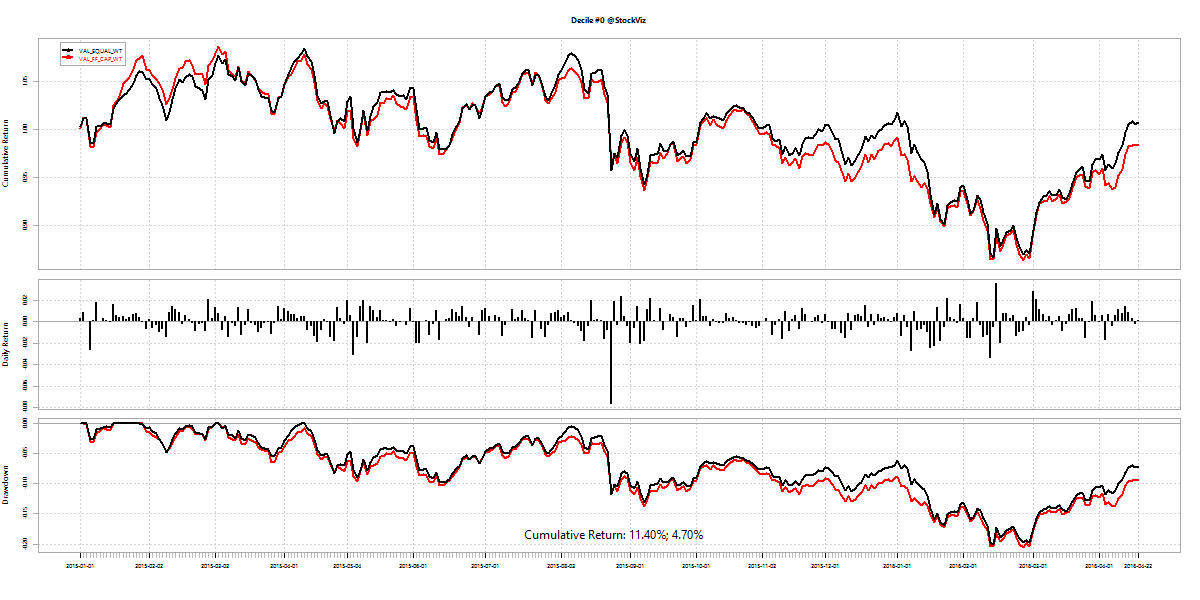
Turnover, defined as volume over total number of shares outstanding, is not constant throughout the day. If you plot turnover over a trading day, it typically traces a ‘U’ shaped plot.
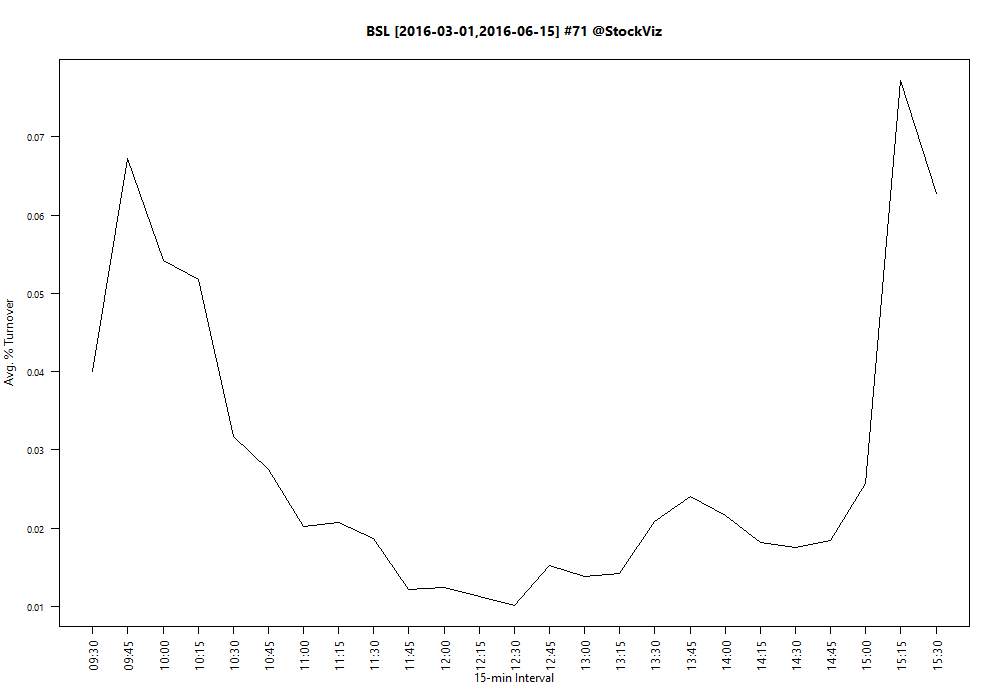
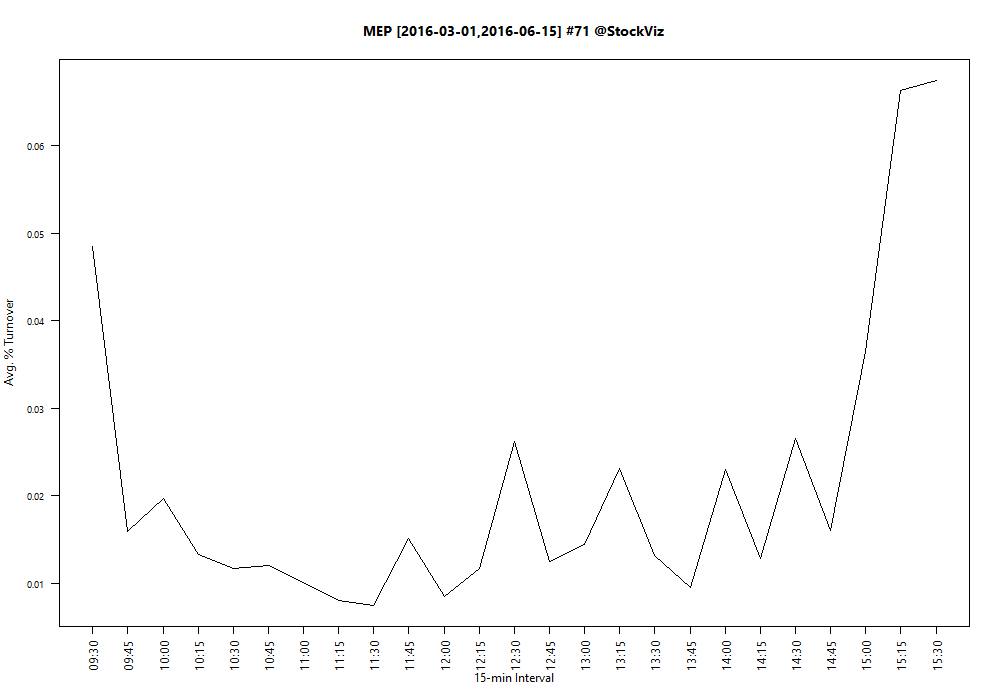
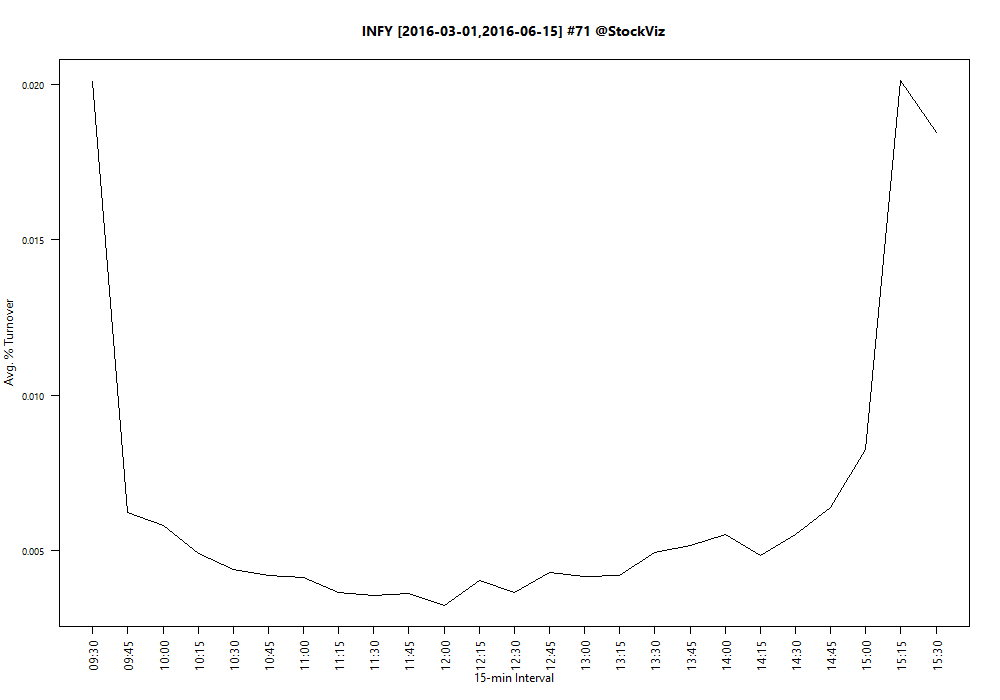
Notice how turnover is the highest in the first half-hour and the last-half hour of trading? Turns out, it is a global phenomena. It follows that if you want liquidity, then it is enough if you show up for the last half-hour of trading.
Related:
Trading Day of Month Returns
Equity Returns at the Turn of the Month
Improving VWAP Strategies: A Dynamic Volume Approach