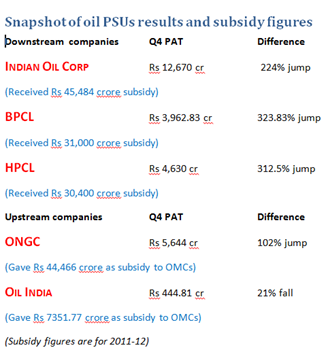
Headwinds from struggling domestic economy as a result of rising inflation, interest rates, lower profitability and weak demand continue to weigh on corporate India. This has severely impaired their ability to service debt and a record number of companies are knocking on the doors of corporate debt restructuring (CDR) cell to recast their loans.
The total number of debt restructuring cases received by the CDR cell increased from 305 (debt aggregating Rs 1,38,600 crore) as on March-end 2011 to 392 (debt aggregating Rs 2,06,493 crore) at the end of March this year.
The total amount of debt approved for recast by the CDR cell was Rs.1,50,515 crore as of March 31, with new debt of Rs.39,601 crore adding to the sticky loan amount in 2011-12, the highest since the CDR cell was launched in 2001.
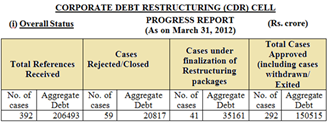 Creditors bring cases to the CDR cell, an informal forum of bankers approved by the Reserve Bank of India, to renegotiate repayment terms with struggling borrowers and help them avert the defaulters tag.
Creditors bring cases to the CDR cell, an informal forum of bankers approved by the Reserve Bank of India, to renegotiate repayment terms with struggling borrowers and help them avert the defaulters tag.
A large number of iron and steel, infrastructure, telecom and textiles companies are in the danger zone. Some of the big-ticket cases that have taken the restructuring route include telecom tower services provider GTL [stockquote]GTLINFRA[/stockquote], shipbuilder Bharati Shipyard [stockquote]BHARTISHIP[/stockquote], Air India, Kingfisher Airlines [stockquote]KFA[/stockquote], Hindustan Construction [stockquote]HCC[/stockquote], Leela Hotel [stockquote]HOTELEELA[/stockquote] and several sugar and steel mills. Jindal Stainless [stockquote]JSL[/stockquote] is the latest entrant to this infamous club. It has approached lenders to reschedule repayments of its over Rs 9,000 crore debt.
Bank loans to large airlines and State Electricity Boards (SEBs) and Discoms (distribution companies) also face the risk of default, though these are currently not under CDR restructuring. Air India’s Rs 22,000 crore CDR and those of SEBs, which is close to Rs.30,000 crore, were restructured outside the cell.
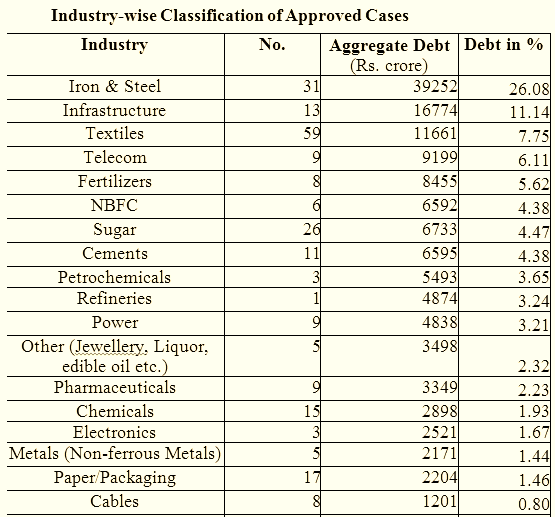
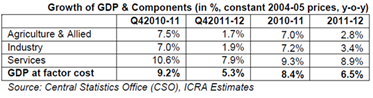
The slowdown in industrial growth resulted from rising input and borrowing costs, due to which investment and consumption growth moderated in interest-sensitive sectors.
 While a slowing economy hurts the ability of companies to repay their debt, some bankers feel many promoters, who have got their loans restructured, are misusing the corporate debt restructuring (CDR) mechanism by passing on their burden to the lenders.
While a slowing economy hurts the ability of companies to repay their debt, some bankers feel many promoters, who have got their loans restructured, are misusing the corporate debt restructuring (CDR) mechanism by passing on their burden to the lenders.
Amidst such dire situations, the government is only doing more harm to lenders. Last month, the centre directed lenders to rejig Rs 35,000 crore of loans to textile firms, adding more restructuring burden on banks. Ideally, the minimum interest rate to which the coupon is reduced to in a restructuring package is the base rate. The package involves bringing debt service coverage ratio to a respectable level, converting part of loan into equity etc.
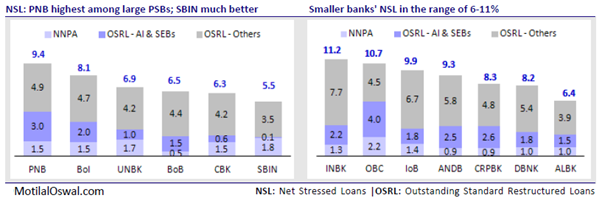
Public sector banks [stockquote]PSUBNKBEES[/stockquote] continued to witness a rise in bad loans during the March quarter due to restructured assets. During the March quarter, SBI [stockquote]SBIN[/stockquote] recast loans worth Rs 5,100 crore against Rs 2,100 crore in the December quarter. Banks have to set aside more money in the form of provisioning on restructured advances, which affects profitability.
The macro environment remains challenging with sluggish business outlook, policy uncertainties, limited access to fund raising avenues for highly leveraged companies and project implementation delays. Clearly, we have not yet seen the worst on bad loans front.