A developing India needs proper supply of electricity to meet the growing demand from households and other sectors and sustain its economic growth. But there is a yawning gap between what is planned and what the power sector has delivered.
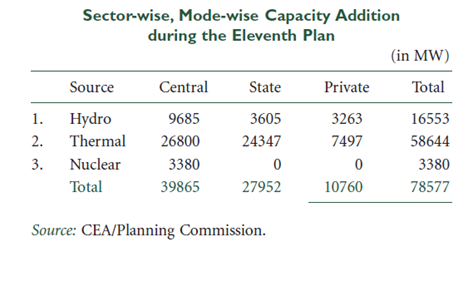
The government had earlier set a goal for adding 78,577 MW of electricity capacity during the 11th Five-Year Plan, which was scaled down to 62,000 MW by the Planning Commission in its mid-term review, citing environmental and land acquisition hurdles.
Other issues that have plagued the power sector include shortage of fuel, distorted prices of electricity, worsening health of power distribution companies, higher transmission and distribution (T&D) losses among others.
According to the Association of Power Producers (APP), a grouping of over 20 private power companies in the country, an estimated 52 power projects having total capacity of 68,563 megawatts are facing default risks at present.
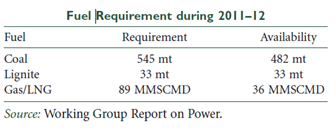 Coal-fired plants, which account for 55.9% of the country’s total power-generating capacity, are facing a severe scarcity of the fuel. The demand-supply gap for coal, which stood at 84 million tonnes (MT) last fiscal, is likely to touch 142 MT in the current financial year.
Coal-fired plants, which account for 55.9% of the country’s total power-generating capacity, are facing a severe scarcity of the fuel. The demand-supply gap for coal, which stood at 84 million tonnes (MT) last fiscal, is likely to touch 142 MT in the current financial year.
Coal India [stockquote]COALINDIA[/stockquote], which accounts for 80% of the country’s output, aims to produce 464 million tonnes in 2012/13, and has already scaled down output target to 440 million tonnes in 2011/12.
Coal India’s inability to ramp up output forced the PMO to intervene and direct the state run energy major to sign compulsory supply pacts with power companies.
Starved of fuel, power firms have been importing coal from Australia and Indonesia. Last month, a Bloomberg report noted that India is poised to surpass China as the world’s top importer of thermal coal with purchases exceeding 118 million tonnes this year in India compared with China’s 102 million tonnes. Domestic fuel shortage has led to increased reliance on imported coal for fuelling the additional power capacity.
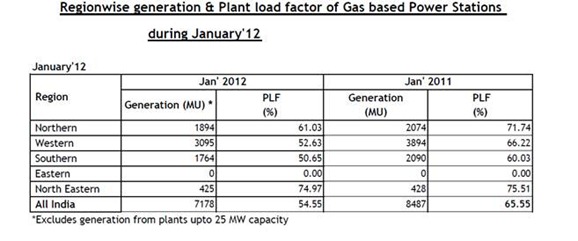
Even as coal supply has run dry, other sources like gas have failed to bridge the supply gap.
With each passing day, gas production from RIL’s prized KG~D6 basin has been hitting new lows. Output stood at 41mmscmd in Q3 FY2012 compared to 45mmscmd in Q2 FY2012. Due to lack of gas from RIL’s block, several gas-based power projects by Reliance Power[stockquote]RPOWER[/stockquote], Lanco [stockquote]LITL[/stockquote] and GMR [stockquote]GMRINFRA[/stockquote] in Andhra Pradesh are sitting idle.
The Power Ministry’s pet project, Ultra Mega Power Projects (UMPPs), each of which is 4000 MW, face an additional problem of financing as lenders are unwilling to bear the risks associated with the execution of such large projects.
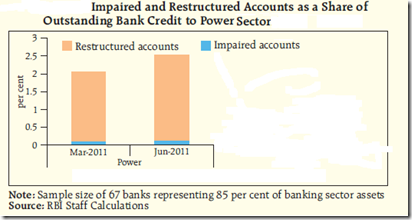
The fallout of these multiple set of problems has been an increase in impairments and restructuring of loans to the power sector.
Since the power sector is considered as a catalyst for economic growth, hard-core reforms are needed to make the sector more efficient and meet the heavy demand for electricity.
Policies must be evolved to ensure completion of on-going projects quickly and add new capacity in an efficient, least cost manner, greater reliance on renewable energy like wind and solar power, easy access to long-term finance, assured supply of coal and gas and an efficient distribution system.