Too much of anything is bad. India’s unending appetite for gold is also proving to be its nemesis.
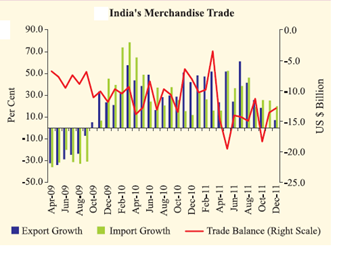 Trade deficit for 2011-12 (April-January) at $ 148.7 billion was 40.4 per cent higher than $ 105.9 billion in 2010-11 (April- January). While higher oil import bill is largely a known factor, the sharp increase in import of gold and silver has intensified pressure on trade deficit (exports minus imports).
Trade deficit for 2011-12 (April-January) at $ 148.7 billion was 40.4 per cent higher than $ 105.9 billion in 2010-11 (April- January). While higher oil import bill is largely a known factor, the sharp increase in import of gold and silver has intensified pressure on trade deficit (exports minus imports).
From April to December during the current fiscal (2011-12), imports of gold and silver surged by 53.8% to $45.5 billion. Higher gold imports increases the country’s external financing needs as it would require more foreign exchange to foot the import bill. The share of gold and silver in import basket has risen from 9.3% in 2000-01 to 13.3% in the first half of 2011-12.
Despite record high prices, India was largest consumer of gold in 2011 with total demand of 933.4 tonnes, according to the World Gold Council, down only moderately from 1,000 tonnes in 2010. Apart from traditional factors, high inflation has prompted many investors to switch to gold from financial savings.
![clip_image001[17]](http://stockviz.biz/wp-content/uploads/2012/03/clip_image00117_thumb.png) The fallout of this buying binge by bullion buffs has forced Finance minister Pranab Mukherjee to double the basic customs duty on gold bars to 4%, revising the cost upwards by up to Rs 1,040 per 10 grams. This is the second increase in the last two months to moderate demand. Blaming the sharp surge in imports of gold and other precious metals during the first three quarters of the year for driving the current account deficit (CAD), Mukherjee also intends to charge 2% on jewellery purchases of more than Rs 200,000 along with an excise of 1% on non-branded jewellery. CAD stood at 2.9 per cent in 2010-11 and is expected to be around 3.6 per cent this year.
The fallout of this buying binge by bullion buffs has forced Finance minister Pranab Mukherjee to double the basic customs duty on gold bars to 4%, revising the cost upwards by up to Rs 1,040 per 10 grams. This is the second increase in the last two months to moderate demand. Blaming the sharp surge in imports of gold and other precious metals during the first three quarters of the year for driving the current account deficit (CAD), Mukherjee also intends to charge 2% on jewellery purchases of more than Rs 200,000 along with an excise of 1% on non-branded jewellery. CAD stood at 2.9 per cent in 2010-11 and is expected to be around 3.6 per cent this year.
Fearing more pressure in the country’s CAD, the Prime Minister’s Economic Advisory Council (PMEAC)’s economic report called for discouraging unproductive imports like gold by making other financial assets like mutual funds and insurance attractive.
But will Indians go beyond gold? In these times of downgrades, defaults and debt crisis, ‘yellow fever’ is only likely to spread further.

[stockquote]GOLDBEES[/stockquote]
![clip_image001[7]](http://stockviz.biz/wp-content/uploads/2012/03/clip_image0017_thumb.png)
![clip_image001[19]](http://stockviz.biz/wp-content/uploads/2012/03/clip_image00119_thumb.png)
![clip_image001[6]](http://stockviz.biz/wp-content/uploads/2012/03/clip_image0016_thumb.png)